2025 Performance-Recoverable Closed-Loop Neuroprosthetic System
본문
- Journal
- Advanced Materials
- Page
- DOI: 10.1002/adma.202503413
- Year
- 2025
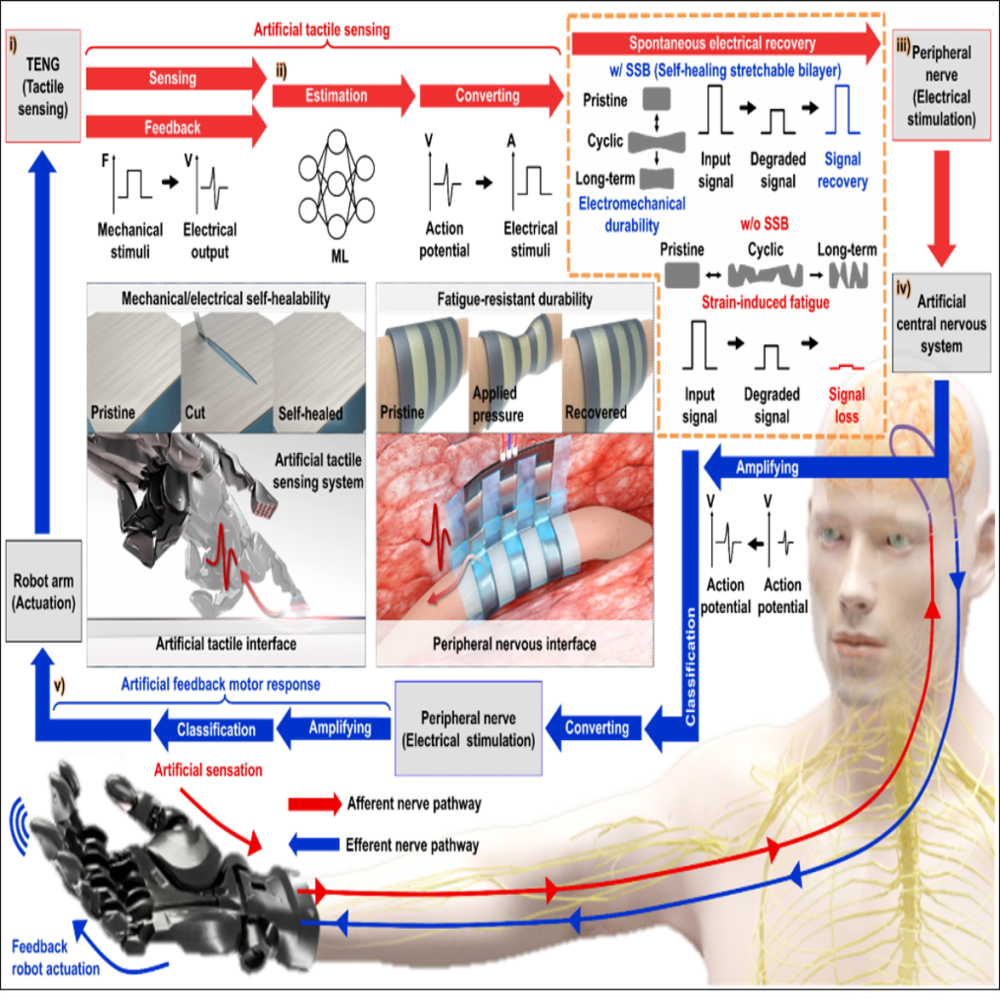
Soft bioelectronics mechanically comparable to living tissues have driven advances in closed-loop neuroprosthetic systems for the recovery of sensory-motor functions. Despite notable progress in this field, critical challenges persist in achieving long-term stable closed-loop neuroprostheses, particularly in preventing uncontrolled drift in the electrical sensitivity and/or charge injection performance owing to material fatigue or mechanical damage. Additionally, the absence of an intelligent feedback loop has limited the ability to fully compensate for sensory-motor function loss in nervous systems. Here, a novel class of soft, closed-loop neuroprosthetic systems is presented for long-term operation, enabled by spontaneous performance recovery and machine-learning-driven correction to address the material fatigue inherent in chronic wear or implantation environments. Central to this innovation is the development of a tough, self-healing, and stretchable bilayer material with high conductivity and exceptional cyclic durability employed for robot-interface touch sensors and peripheral-nerve-adaptive electrodes. Furthermore, two central processing units, integrated in a prosthetic robot and an artificial brain, support closed-loop artificial sensory-motor operations, ensuring accurate sensing, decision-making, and feedback stimulation processes. Through these characteristics and seamless integration, our performance-recoverable closed-loop neuroprosthesis addresses challenges associated with chronic-material-fatigue-induced malfunctions, as demonstrated by successful in vivo under 4 weeks of implantation and/or mechanical damage.