2025 In-sensor multilevel image adjustment for high-clarity contour extraction using adjustable synaptic phototransistors
본문
- Journal
- Science Advances
- Vol
- 11
- Page
- adt6527
- Year
- 2025
- Link
- https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.adt6527 357회 연결
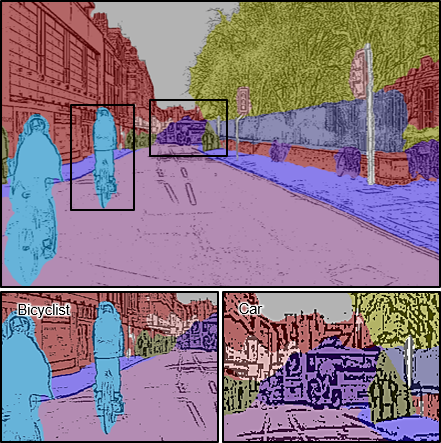
Robotic vision has traditionally relied on high-performance yet resource-intensive computing solutions, which necessitate high-throughput data transmission from vision sensors to remote computing servers, sacrificing energy efficiency and processing speed. A promising solution is data compaction through contour extraction, visualizing only the outlines of objects while eliminating superfluous backgrounds. Here, we introduce an in-sensor multilevel image adjustment method using adjustable synaptic phototransistors, enabling the capture of well-defined images with optimal brightness and contrast suitable for achieving high-clarity contour extraction. This is enabled by emulating dopamine-mediated neuronal excitability regulation mechanisms. Electrostatic gating effect either facilitates or inhibits time-dependent photocurrent accumulation, adjusting photo-responses to varying lighting conditions. Through excitatory and inhibitory modes, the adjustable synaptic phototransistor enhances visibility of dim and bright regions, respectively, facilitating distinct contour extraction and high-accuracy semantic segmentation. Evaluations using road images demonstrate improvement of both object detection accuracy and intersection over union, and compression of data volume.